SolasCure gel vetted by US military to combat war wounds

SolasCure is a Cambridge biotech company developing a novel treatment to transform chronic wound care. The US collaboration will evaluate Aurase which is a hydrogel releasing tarumase, a recombinant enzyme derived from medical maggots, which is currently being developed to promote wound healing through debridement and wound bed preparation.
In partnership with USAISR, two non-clinical development projects will be initiated to assess the potential for the enzymatic debridement properties of Aurase Wound Gel to reduce wound biofilm production and/or bioburden in conjunction with standard-of-care in prolonged field care scenarios.
Opportunistic pathogens such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa and MRSA complicate wound care by producing toxins and enzymes that damage tissue. They often lead to chronic infections that are hard to eradicate due to biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance. The projects aim to specifically target combat-relevant persistent strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and MRSA both in vitro and in vivo.
AISR is recognised as the U.S. Army’s premier research laboratory for improving the care of combat casualties. The collaboration aims to generate non-clinical data that could be used as a first step to validate the use of Aurase Wound Gel in highly challenging combat conditions.
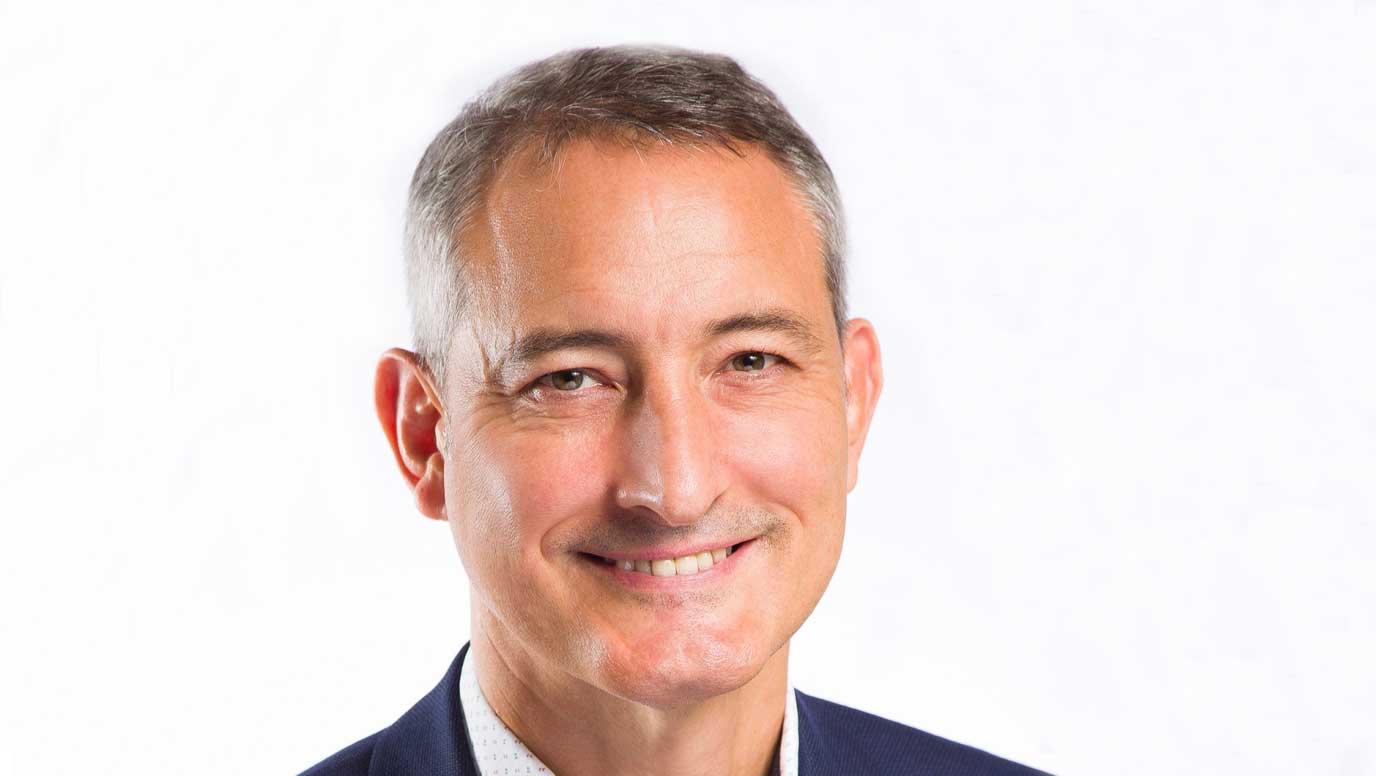
SolasCure CEO, Lee Harle, said: “It is an honour that the US military, one of the most prestigious and impressive institutions globally, has identified our technology and chosen to support its ongoing development. We look forward to the outcome of the projects to assess the suitability of Aurase Wound Gel for managing biofilm and bioburden in prolonged combat situations.”